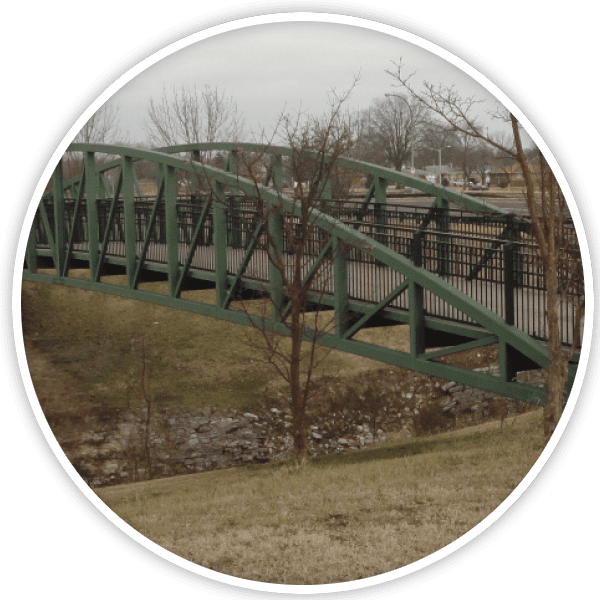
 Bridge crossings over roadways or waterways should be provided where the trail alignment intersects these features and where an alternative alignment cannot be resolved through traditional methods or to alleviate pedestrian-vehicular conflicts.
Bridge crossings over roadways or waterways should be provided where the trail alignment intersects these features and where an alternative alignment cannot be resolved through traditional methods or to alleviate pedestrian-vehicular conflicts.
Narrow and/or shallow water bodies such as small streams, ditches, or wetlands can be crossed with Boardwalks or by using Culverts to maintain flow. Applications for bridges may vary based on site-specific constraints, budgetary constraints, or infrastructure to be used. However, the following standards should be implemented:
- When bridges cross roadways, connections to the roadway pedestrian and bicycle facilities should be made, if possible.
- Bridges should be designed to facilitate maintenance/emergency vehicles.
- ADA compliance shall be included in bridge approaches, the bridge surface and railings, and connections to existing pedestrian and bicycle facilities.
- Ensure transition from bridge to trail is smooth across the width of the trail. There are to be no steps and no bumps.
- Steel, prefabricated bridges are the preferred bridging.
- Bridges to be unpainted, weathered steel.
Design metrics:
- Standard Width: Bridge deck should be a minimum width of the approach trail (12’-0”)
- Vertical Clearance: 8’ minimum, 10’ where maintenance/emergency vehicle use is anticipated.
- Deck Height: Where feasible the bridge deck is to be placed above the 10-year flood elevation. If this cannot be met then the bridge deck should be placed as far above the crossing waterbody as is feasible.
- Railing Height: 48” minimum, up to 54” where conditions warrant increased protection. A smooth, wide rub rail should be provided from 36”-44” where the bicyclist’s handlebars could come in contact with the railing. Extend railing past abutment as needed to protect trail users from fall hazards, min. 6’, typ.
- Landings: All transitions shall be ADA compliant. Use methods to mitigate erosion or settling where the trail surface meets the bridge landing.
- Erosion Control: Bridges require temporary and permanent erosion controls including bridge scour protections. Temporary erosion controls are typically implemented during construction and keep sediment and debris from leaving the construction site. Permanent erosion controls include, but are not limited to, streambank stabilization, bridge scour protections, and controls to prevent or mitigate deterioration of the trail surface at the bridge landing. See Bridge Scour Protections for more guidance.
- Design Load: H5 (10,000 lb) for ambulance or fire rescue apparatus.
Environmental Graphics
Bridges provide a valuable opportunity for the installation of visual elements that elevate brand awareness, enhance user experience and communicate interpretive messages. Great Rivers Greenway has created an environmental graphics toolkit that contains various designs and elements that can be considered during the planning and design process.
STANDARD PLAN DIAGRAM
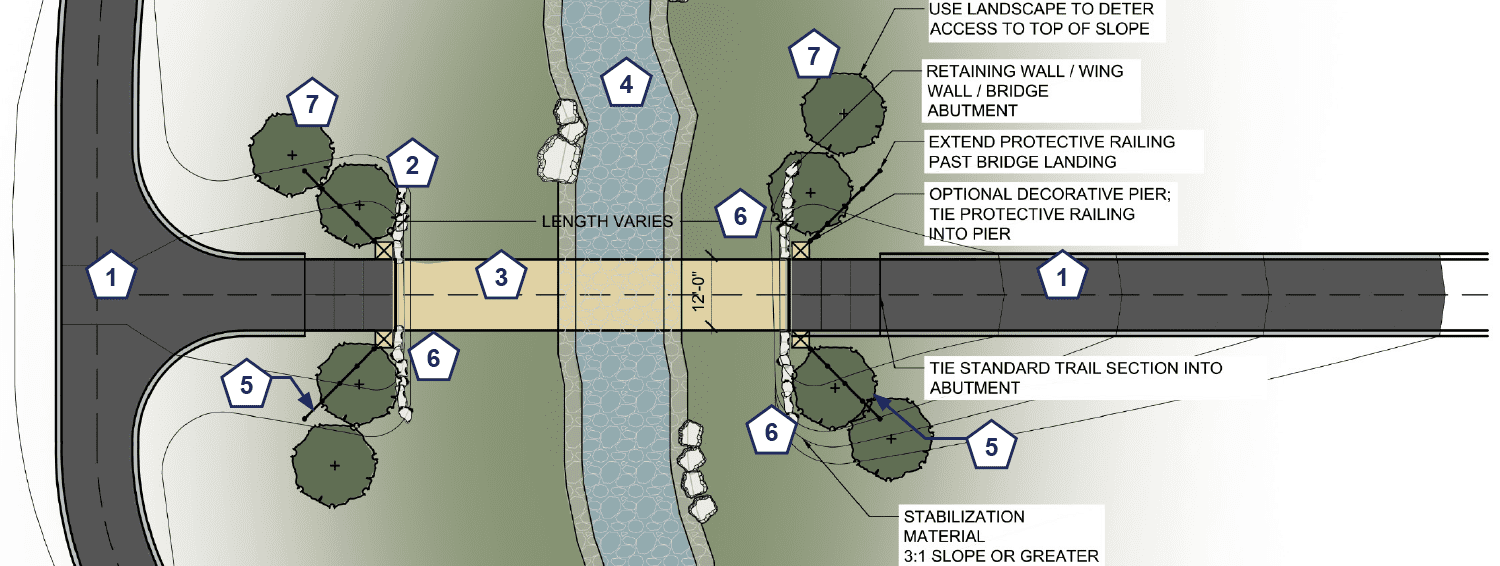
FEATURE COMPONENTS:
1) Trail
2) Abutment
3) Bridge Surface
4) Existing waterway/roadway
5) Railings
6) Bank stabilization strategy
7) Plantings